
Sarthak Tyagi
Web Developer | AWS Cloud Architect

Learn how to develop healthcare software with our comprehensive guide. Discover step-by-step processes, case studies, and market trends to succeed in 2025.
In the rapidly evolving healthcare industry, software solutions are pivotal for enhancing patient care, streamlining operations, and ensuring compliance with stringent regulations. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, healthcare software empowers organizations to deliver efficient, high-quality services. However, developing such software can be complex, requiring technical expertise, regulatory knowledge, and a focus on user needs. For founders, owners, entrepreneurs, and CEOs, navigating this process can seem overwhelming, particularly without a technical background.
This comprehensive guide simplifies healthcare software development, offering a step-by-step approach tailored for business leaders. By following these steps, you can create software that meets regulatory standards, addresses specific healthcare challenges, and drives measurable outcomes. Supported by real-world case studies and market statistics, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and leverage technology for competitive advantage.
Healthcare software encompasses applications designed to improve medical service delivery and management. Key types include:
These solutions must comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, ensuring data privacy and security. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, making regulatory adherence a critical consideration.
Developing healthcare software requires a structured approach to ensure functionality, compliance, and user satisfaction. Below is a detailed guide to the process.
Begin by identifying the specific needs your software will address. Engage stakeholders—doctors, nurses, administrators, and IT staff—to gather insights. Consider:
Create a prototype to visualize the software’s functionality. This involves:
Present the prototype to users for review. Focus on:
With feedback incorporated, proceed to design and development. Key considerations include:
Rigorous testing is essential to ensure reliability and security. This includes:
Based on testing results, refine the software. This involves:
Deploy the software and provide ongoing support:
Businesses must decide between custom-developed software and off-the-shelf solutions. The table below compares these approaches:
| Aspect | Custom Development | Off-the-Shelf Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher upfront, potentially lower long-term | Lower upfront, possible subscription fees |
| Time to Market | Longer development time (3-12 months) | Faster deployment (weeks to months) |
| Flexibility | Tailored to specific needs | Limited customization options |
| Compliance | Designed for specific regulations | May require adjustments for compliance |
| Scalability | Built to scale with business growth | May have scalability limitations |
| Support | Requires in-house or contracted support | Typically included in subscription |
Custom development is ideal for unique needs or complex integrations, while off-the-shelf solutions suit businesses needing quick, cost-effective deployment for standard functionalities.
The following case studies illustrate the impact of healthcare software development across diverse applications.
Overview: A U.S.-based provider with 20 hospitals and 150 clinics implemented a unified EHR system with AI-powered predictive analytics and telemedicine capabilities.Outcome: Achieved a 30% improvement in operational efficiency, a 20% increase in patient satisfaction, and a 15% reduction in hospital readmissions.Source: DigitalDefynd Case Studies
Overview: A European healthcare network deployed a cloud-based EHR, data analytics, and a digital patient portal with machine learning algorithms.Outcome: Improved efficiency by 40%, increased patient portal usage by 25%, and reduced diagnostic inaccuracies by 20%.Source: DigitalDefynd Case Studies
Overview: A Canadian provider developed a centralized digital platform with upgraded telehealth and big data analytics.Outcome: Gained 30% operational efficiency, 25% higher patient satisfaction, 35% reduction in administrative efforts, and a 50% surge in telehealth adoption.Source: DigitalDefynd Case Studies
Overview: An Australian network implemented a unified digital health platform with telehealth, AI-driven diagnostics, and IoT devices.Outcome: Achieved 40% administrative efficiency, a notable increase in patient satisfaction, 60% greater patient reach, and 30% improved treatment outcomes.Source: DigitalDefynd Case Studies
Overview: A U.S.-based provider developed an advanced EHR with AI analytics, a patient mobile app, and real-time resource tracking.Outcome: Improved clinical efficiency by 45%, increased app usage by 30%, reduced patient wait times by 50%, and minimized medical errors.Source: DigitalDefynd Case Studies
These examples highlight how tailored software solutions drive efficiency, enhance patient experiences, and support scalability.
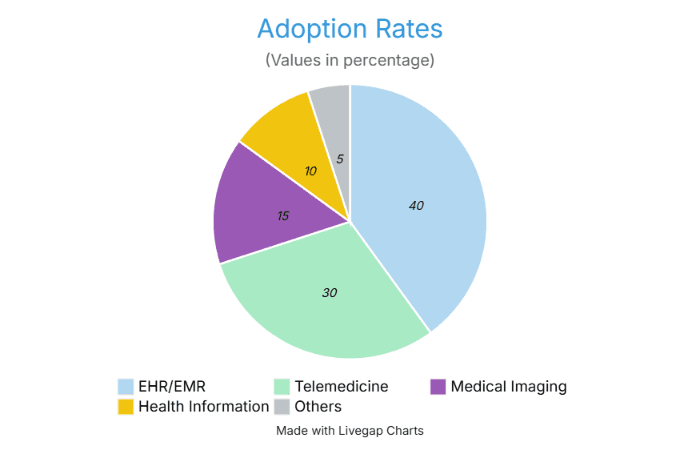
The healthcare software market is experiencing robust growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for digital solutions. Below are key statistics and trends:
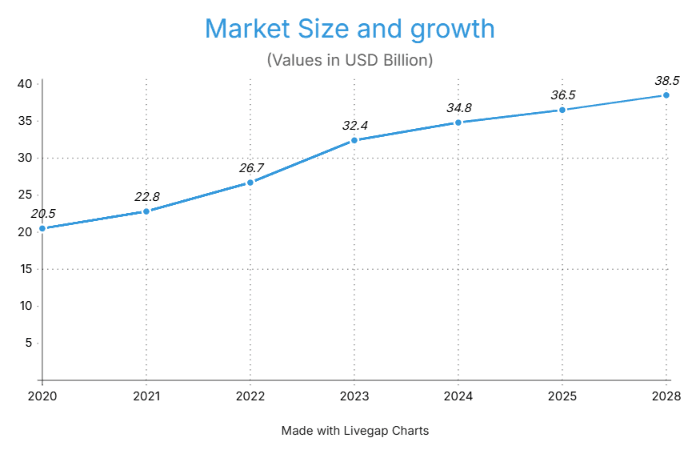
Image by Gautam IT Services
© Gautam IT Services
North America holds a 40% revenue share in the global healthcare IT market, driven by U.S. adoption of EHRs and federal mandates like the HITECH Act (Grand View Research, 2024).
These trends underscore the growing importance of healthcare software, offering opportunities for businesses to innovate and capture market share.
Healthcare software development, while complex, can be streamlined with a structured approach. By defining clear requirements, prototyping, gathering feedback, and ensuring rigorous testing, businesses can create solutions that enhance patient care and operational efficiency. Choosing between custom and off-the-shelf solutions depends on specific needs, budget, and timeline, but both can deliver significant value when implemented strategically.
The case studies demonstrate real-world success, with efficiency gains of 30-45% and patient satisfaction increases of 20-45%. With the healthcare software market projected to grow from USD 34.8 billion in 2024 to USD 38.9 billion by 2028, now is the time for founders, owners, entrepreneurs, and CEOs to invest in these technologies. Start your journey today to transform healthcare delivery and stay ahead in a competitive landscape.